64 Entries : Results for 연구
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
http://ni.lithium.com/t5/Multifunction-DAQ/Residual-voltage-on-AO-channel/m-p/217699/highlight/true#M12457
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ Intro
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80069903296
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제1강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80069905393
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제2강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80070080150
랩뷰기본설정
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제3강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80072385941
데이터타입
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제4강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80086513649
데이터타입 숫자형
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제5강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80087108527
데이터타입 불리언, 문자열
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제6강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80087389534
데이터타입 컨트롤, 인디케이터
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 부록1
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80087452003
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제7강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80090203111
데이터타입 배열, 클러스터, 행렬
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제8강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80090370964
숫자형함수
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제9강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80090777826
숫자형함수 (몫&나머지, 복합연산, 식 노드, 변환)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제10강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80092309292
숫자형함수 변환
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제11강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80092423712
숫자형함수 변환, 복소수, 상수
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제12강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80092581048
코딩빨리하기
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제13강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80092857122
구조함수, For루프, While루프
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제14강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80093039293
구조함수, For루프, While루프 (시프트 레지스터)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제15강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80094291821
구조함수, For루프, While루프 (타이밍)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제16강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80094358841
구조함수, For루프, While루프 (오토 인덱싱)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제17강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80094521098
구조함수, 케이스구조 (조건 터미널 : 숫자형)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제18강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80094801865
구조함수, 케이스구조
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제19강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80094960306
구조함수, 시퀀스구조 (레이스 컨디션)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제20강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80095255625
구조함수, MathScript노드, 수식노드
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제21강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80095408795
디버깅 (실행 하이라이트, 프로브, 단계별 실행, 브레이크 포인트)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제22강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80095876339
불리언함수
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제23강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80096391255
비교함수 (선택함수, 최대최소 함수, 범위내 확인과 강제변환)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제24강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80096518012
배열함수 (배열 크기, 배열 인덱스. 배열 부분 대체, 배열에 삽입, 배열로부터 삭제, 배열 잘라내기, 배열 초기화, 배열 만들기)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제25강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80096878459
배열함수 (배열 최대 최소, 배열 차원 변경, 1D 배열 정렬, 1D 배열 검색, 1D 배열 분리, 1D 배열 뒤집기, 1D 배열 회전, 1D 배열 보간)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제26강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80104036995
배열함수 (1D 배열 임계점, 1D 배열 끼워넣기, 1D 배열 부분제거, 2D 배열 전치, 배열을 클러스터로)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 부록1
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80104245006
강제변환점
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 부록1
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80104841704
단축키 (각주)
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제27강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80105748741
에러핸들링
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제28강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80107230634
타임스탬프, UI꾸미기
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제29강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80107412352
타이밍함수 (틱 카운트, 기다림, 다음 ms 배수까지 기다림,
랩뷰(LabVIEW)프로그래밍 튜토리얼_ 제30강
http://blog.naver.com/vikaly/80112872740
타이밍함수, 숫자형컨트롤 (날짜 / 시간을 초로 얻기, 문자열로 얻기,
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
저도 이런거 비슷한 걸 하고 있습니다...
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
무더운 여름이 시작되는 요즈음 회원 여러분들의 건승하심을 기원합니다.
다름이 아니오라 물리학회 영문 학술지인 Journal of the Korean Physical Society (JKPS)의 현재 상황과 함께 향후 대책을 회원 여러분께 알려 드리고자 합니다.
이 미 주지하시다시피 JKPS는 2009년도 ISI Thomson사에 의해 impact factor가 발표되지 않았으며 2010년까지 2년간 그 상태가 유지되도록 결정되어 있습니다. 저희 편집진에서는 다방면으로 노력을 기울여 이 상황을 1년 만에 특별종료 시키려고 하였으나, ISI Thomson사의 규정에 따라 JKPS의 impact factor는 무슨 이유라도 2년 동안 발표되지 않는다는 통보를 받았습니다. 저희 편집진에서 기울인 노력에도 불구하고 올해에도 impact factor가 발표되지 않은 것에 대해 회원 여러분께 송구스러운 마음을 금할 길이 없습니다.
다만 한 가지 반가운 사실은 저희 편집진이 자체 개발한 프로그램으로 JKPS의 인용 현황을 예의 주시하고 있는데 자기인용(self citation) 비율이 2008년 73.9%에서 2009년 70.3% 그리고 2010년 6월 현재 50% 수준으로 지속적으로 감소하여 ISI Thomson사가 요구하는 자기인용 비율 이하로 크게 개선되었습니다. 이러한 추세를 유지한다면 내년에는 당연히 JKPS의 impact factor가 다시 발표되는 상황으로 될 것으로 확신합니다. 하지만 이렇게 자기인용 비율은 감소하였으나 필연적으로 JKPS의 impact factor가 어느 정도 떨어질 것이 우려됩니다. JKPS의 impact factor가 많이 떨어지지 않도록 회원 여러분의 큰 관심과 격려를 부탁드립니다. 특히 회원 여러분께서 다른 저널에 논문을 투고하실 때 JKPS에 출판된 논문을 되도록 많이 인용하여 주실 것을 다시 한 번 간곡히 부탁드립니다.
JKPS의 impact factor가 발표되지 않는 상황으로 BK21 평가 등 국책연구과제의 평가에서도 불이익을 당하고 있습니다. 이러한 상황의 개선에 일조 하고져 물리학회 회장단과 편집진이 지난 6월 16일 한국연구재단을 방문하여 이 문제를 의논한 결과, 2011년 BK21 평가 이전에 ISI Thomson사로부터 JKPS의 impact factor가 2011년부터 다시 발표될 것이라는 공식 통보를 받으면, 비록 2011년 impact factor가 발표되는 시기(보통은 매년 6월경에 발표됨)보다 앞서서 BK21 평가(보통 4월에서 5월경에 이루어짐)가 이루어지더라도 JKPS의 경우 2007년도 impact factor를 이용하여 평가하기로 협의되었습니다.
다시 한 번 이러한 일로 회원 여러분께 걱정을 끼쳐드려 대단히 죄송합니다. JKPS에 대한 애정을 끝까지 지켜 주시고 더욱 도와주시기를 부탁드립니다.
한국물리학회 JKPS 편집위원장 이 주 열
한국물리학회 회장 이 영 백

- Tag jkps
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
http://www.2010ispqt.org/index.htm
10th Asian Conference on Quantum Information Science
http://www.qci.jst.go.jp/aqis10/index.html
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
http://www.endnote.com/
근데 사실 이거말고도 서지정보를 관리하는 프로그램은 여러가지가 있는데도 불구하고 굳이 엔드노트를 사용했던건 UI가 편한것보다는, 다른 학교들도 대부분 다 그렇겠지만, 학교에서 Thomson사와 계약해서 엔드노트 프로그램을 쓸수있게 라이센스를 구입했기 때문이었다. 2009년부터는 계약이 종료된 모양이지만 뭐 그건 나랑 상관없으니...
그런데 개인적으로 Endnote는 솔직히 그렇게 편리한 툴은 아니었다.
우선은 서지정보를 입력하는게 좀 귀찮다. 구글 스콜라에서 endnote로 export되도록 설정한뒤 검색한 후 export 파일을 받아서 endnote에서 import해야 한다. endnote가 열려있는 상태라면 import작업이 바로 시작되어 주지만 endnote는 항상 켜놓는 류의 프로그램은 아니기 때문에 안열어놓고 검색하는 일이 비일비재하다.
두번째는 노트입력이 불편하다.
PDF파일에 노트를 기입하는 건 endnote차원의 문제가 아니니 넘어가고, 서지정보 리스트가 표시된 상태에서 논문을 간단하게 요약한다든지 하는 노트를 기입해서 볼수있게 하는 기능이 필요한데 이상하게도 endnote는 서지정보에서 note항목에 이걸 입력해도 리스트화면에서 나타나지 않으며 나타나게 할수도 없다. 그래도 노트는 필요해서 나같은 경우 위키페이지를 만들어서 서지당 노트를 기입하고 그걸 endnote에서 URL연결시키는 뻘짓까지 했다.
세번째는 그룹관련인데,
그룹의 하위그룹을 만들수가 없다. 엄청나게 기본적이고 또한 중요한 기능인데도 불구하고 최근버전인 X3에 와서야 추가되었다고 한다. 이런 한심할데가...
하여튼, 동대에 입학하게되면서 이전 서지정보를 가져올려고 그랬더니 동대는 endnote 패키지판은 제공하지 않고 웹버전의 계정만 제공한다고 한다. 비싼 계약료를 다 지불할 필요가 없었다고 생각한 모양이다.
https://www.myendnoteweb.com/
뭐 좋다, 그래서 계정 등록하고 쓸려고 그랬는데 이건 더 불편하다.
우선은 구글 스콜라에서 import가 안된다. ISI나 SCOPUS같은 페이지를 통한 검색결과의 import만 된다.
근데 써보면 알겠지만 ISI에서 검색된게 SCOPUS에서 안되는것도 있고 그 반대도 있고 그렇다. 논문은 구글에서 찾아놓고 서지정보 입력할려고 ISI들어가서 다시 검색하고 없어서 SCOPUS 들어가고 하는 뻘짓을 해야한다. 그렇다고 입력된 데이터를 가공하기 좋냐하면 그것도 아니다. web 기반이라 데이터공유는 쉽지만 web인만큼 느리기도 느리고 뭐 어쨌든 존내 쓰기 불편하다.
그래서 이전부터 계속 검토는 해 오고 있던 Zotero를 설치했는데 결론부터 말하자면, 아주아주 쓸만하다.
파이어폭스 애드온이라 뭐 얼마나 강하겠어? 하는 생각이었는데 막상 써보고 나니 톰슨이 소송건 이유를 알것 같다.
https://kldp.org/node/99214
연구행위를 할때는 endnote를 24시간 켜놓지는 않지만 웹브라우저는 24시간 켜놓는다. 그 사실에 착안했는지 어쨌는지 Zotero는 전세계적으로 사랑받는 웹브라우저 파이어폭스의 애드온이라는 형식을 취했고 그 덕분에 파폭을 사용하는 사람은(나 포함) 이 프로그램을 24시간 돌리게 된다는 말이 된다.
애드온이므로 그리 무거울 일도 없고, Zotero서버에 PDF를 제외한 서지정보가 저장되기 때문에 인터넷이 되는곳이라면 어디라도 동일하게 싱크된 서지정보 데이터베이스를 이용할 수 있다. 할려고 마음먹으면 PDF도 웹에 저장할수 있지만(http://www.zotero.org/support/storage_faq) WebDAV 서버가 있으면 PDF를 거기에 보존할 수도 있다. Zotero에서 공식 언급하고 있는 무료계정http://www.zotero.org/support/sync#file_syncing
중 하나 (cloudMe, JungleDisk, BingoDisk etc.)로 cloudme 서비스가 있다.
https://www.cloudme.com/
cloudme 계정은 아무래도 업체측에서 zotero를 공식 지원하는 모양으로 조테로관련 글에 어드민이 답변을 달아주고 있다.
http://forum.cloudme.com/viewtopic.php?id=416
공식 설정법도 나와있음
https://www.cloudme.com/en/webdav/help
어쨌든 나는 qna에 나와있는 방법을 써서 싱크하고 있는데 잘 된다.
http://webdav.cloudme.com:80/username/xios/zotero
Zotero의 최대장점은 뭐니뭐니해도 서지정보 import 기능인데, 논문 사이트에 들어가면 주소창에 Zotero 아이콘이 뜬다. 이걸 클릭하면 서지정보가 저장된다.
끝이다. 이게 끝인것이다!
Zotero가 import를 지원하는 사이트는 다음과 같다.
http://www.zotero.org/translators
얼마나 다양한 Citation style을 지원하는지도 중요하다. 이렇게 많은 포맷을 지원하고 있다.
http://www.zotero.org/styles
스타일이 없을경우 엔드노트의 스타일파일을 import 할 수도 있는데 소송걸린 이후 X시리즈에서 만든 파일은 import 할 수 없게 되었다. 하여튼 쪼잔하기는...
문제는 지금까지 만들어 온 Endnote 데이터를 import 할수 있는가?
결론부터 말하자면, 된다. PDF까지 다 가져올 수 있다.
간단하게 말하자면 Endnote에서 RIS형식으로 서지정보를 export하면 zotero에서 읽어들일 수 있고 RIS파일속의 PDF경로를 하드디스크 경로로 정확하게 바꾸어주면 PDF까지 같이 import 해준다. 좀 더 자세한 설명이 필요하면 아래를 참조할 것.
http://www.zotero.org/search/type/support/q/endnote%20import
조테로에 css스킨 설정하기
https://forums.zotero.org/discussion/66421/customizing-5-0-user-interface
https://forums.zotero.org/discussion/70647/dark-theme-for-main-zotero-window-black-background-white-text
추가 : PDF를 외부프로그램으로 열게 하려면 파폭의 about:config에서 extensions.zotero.launchNonNativeFiles;true 로 하면 된다.

- Tag endnote, zotero, 서지정보관리 프로그램
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
표준편차(標準偏差)는자료의 산포도를 나타내는 수치로, 분산의 제곱근으로 정의되며 표준 편차가 작을수록 평균값에서 변량들의 거리가 가깝다. 일반적으로 모집단의 표준편차는 σ(시그마)로, 표본의 표준편차는 S(에스)로 나타낸다.
http://blog.naver.com/thegoldman/30067191786
=stdev(범위)
*상대표준편차(RSD : Relative Standard Deviation)
상대표준편차란 표준편차를 평균으로 나눈 후 100을 곱한 수치로서 변동계수(CV : Coefficient of Variability)라고도 한다. 즉, 상대표준편차가 크다는 것은 표준편차가 평균에 비해 상대적으로 크다는 의미이므로 산포도가 큼을 의미하고 그렇지 않은 경우에는 산포도가 작음을 의미한다. 또한 상대표준편차는 단위가 없는 측도이므로 서로 다른 측정단위를 갖는 데이터 셋의 산포도 비교에 유용하게 사용된다.
=stdev(범위)/average(범위)*100
*표준오차(SE : Standard Error)
각 표본들의 평균이 전체 평균과 얼마나 떨어져있는가를 알려줌.
표준편차 / √(표본 개수)
http://blog.naver.com/nlboman/22643979
http://blog.naver.com/nlboman/56166123
=stdev(범위)/sqrt(count(범위))
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
출처 :PLoS Computational Biology: Ten Simple Rules for Getting Published
Philip E. Bourne
Rule 1: Read many papers, and learn from both the good and the bad work of others.
It is never too early to become a critic. Journal clubs, where you critique a paper as a group, are excellent for having this kind of dialogue. Reading at least two papers a day in detail (not just in your area of research) and thinking about their quality will also help. Being well read has another potential major benefit—it facilitates a more objective view of one's own work. It is too easy after many late nights spent in front of a computer screen and/or laboratory bench to convince yourself that your work is the best invention since sliced bread. More than likely it is not, and your mentor is prone to falling into the same trap, hence rule 2.
Rule 2: The more objective you can be about your work, the better that work will ultimately become.
Alas, some scientists will never be objective about their own work, and will never make the best scientists—learn objectivity early, the editors and reviewers have.
Rule 3: Good editors and reviewers will be objective about your work.
The quality of the editorial board is an early indicator of the review process. Look at the masthead of the journal in which you plan to publish. Outstanding editors demand and get outstanding reviews. Put your energy into improving the quality of the manuscript before submission. Ideally, the reviews will improve your paper. But they will not get to imparting that advice if there are fundamental flaws.
Rule 4: If you do not write well in the English language, take lessons early; it will be invaluable later.
This is not just about grammar, but more importantly comprehension. The best papers are those in which complex ideas are expressed in a way that those who are less than immersed in the field can understand. Have you noticed that the most renowned scientists often give the most logical and simply stated yet stimulating lectures? This extends to their written work as well. Note that writing clearly is valuable, even if your ultimate career does not hinge on producing good scientific papers in English language journals. Submitted papers that are not clearly written in good English, unless the science is truly outstanding, are often rejected or at best slow to publish since they require extensive copyediting.
Rule 5: Learn to live with rejection.
A failure to be objective can make rejection harder to take, and you will be rejected. Scientific careers are full of rejection, even for the best scientists. The correct response to a paper being rejected or requiring major revision is to listen to the reviewers and respond in an objective, not subjective, manner. Reviews reflect how your paper is being judged—learn to live with it. If reviewers are unanimous about the poor quality of the paper, move on—in virtually all cases, they are right. If they request a major revision, do it and address every point they raise both in your cover letter and through obvious revisions to the text. Multiple rounds of revision are painful for all those concerned and slow the publishing process.
Rule 6: The ingredients of good science are obvious—novelty of research topic, comprehensive coverage of the relevant literature, good data, good analysis including strong statistical support, and a thought-provoking discussion. The ingredients of good science reporting are obvious—good organization, the appropriate use of tables and figures, the right length, writing to the intended audience—do not ignore the obvious.
Be objective about these ingredients when you review the first draft, and do not rely on your mentor. Get a candid opinion by having the paper read by colleagues without a vested interest in the work, including those not directly involved in the topic area.
Rule 7: Start writing the paper the day you have the idea of what questions to pursue.
Some would argue that this places too much emphasis on publishing, but it could also be argued that it helps define scope and facilitates hypothesis-driven science. The temptation of novice authors is to try to include everything they know in a paper. Your thesis is/was your kitchen sink. Your papers should be concise, and impart as much information as possible in the least number of words. Be familiar with the guide to authors and follow it, the editors and reviewers do. Maintain a good bibliographic database as you go, and read the papers in it.
Rule 8: Become a reviewer early in your career.
Reviewing other papers will help you write better papers. To start, work with your mentors; have them give you papers they are reviewing and do the first cut at the review (most mentors will be happy to do this). Then, go through the final review that gets sent in by your mentor, and where allowed, as is true of this journal, look at the reviews others have written. This will provide an important perspective on the quality of your reviews and, hopefully, allow you to see your own work in a more objective way. You will also come to understand the review process and the quality of reviews, which is an important ingredient in deciding where to send your paper.
Rule 9: Decide early on where to try to publish your paper.
This will define the form and level of detail and assumed novelty of the work you are doing. Many journals have a presubmission enquiry system available—use it. Even before the paper is written, get a sense of the novelty of the work, and whether a specific journal will be interested.
Rule 10: Quality is everything.
It is better to publish one paper in a quality journal than multiple papers in lesser journals. Increasingly, it is harder to hide the impact of your papers; tools like Google Scholar and the ISI Web of Science are being used by tenure committees and employers to define metrics for the quality of your work. It used to be that just the journal name was used as a metric. In the digital world, everyone knows if a paper has little impact. Try to publish in journals that have high impact factors; chances are your paper will have high impact, too, if accepted.
When you are long gone, your scientific legacy is, in large part, the literature you left behind and the impact it represents. I hope these ten simple rules can help you leave behind something future generations of scientists will admire.

- Tag 논문쓰기
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
...난 내가 폴리스의 '폴'자도 안나오는 기사에 낚였다는 사실을 인정하고 싶지 않아...
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
http://www.eas.caltech.edu/qis2009/photos.html
이 부분이 진짜 하고 싶은 말 아닌가 싶다...(뭐?? 내가 그냥 그랬으면 좋겠다는 거 아니냐고?? ...그럴 수도 있지만 :-P)
http://www.eas.caltech.edu/qis2009/program.html


- Tag qis
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
예상대로 금년 초 QIS회의가 메인이었고, 읽어본 결과 QIS에의 예산삭감 걱정은 안해도 될 것 같다. 어떻게 하면 고용을 더 늘릴까 이런 걱정을 하고 있을 정도인데 뭐...
그것보다도 이번호에는 인문계 애들을 끌어들이는 것에 대해 생각해봐야 한다는 제안이 나왔는데, 이거에 대해서는 언제 한 번 글을 써야 할 것 같다. 아무래도 내가 그 대상이기도 하기 때문에...
원문은 여기서 볼 수 있다.
http://www.aps.org/units/gqi/newsletters/loader.cfm?csModule=security/getfile&pageid=177954
The Quantum Times 그 자체보다 기사속에 들어있는 이 링크가 더 영양가 있을지도...
http://michaelnielsen.org/blog/?p=531

- Tag APS, The Quantum Times
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
*광학과 기술 제11권 제3,4호, 2007. 11
http://www.dbpia.co.kr/view/is_view.asp?pid=788&isid=43855&topMenu=&topMenu1=
http://www.dbpia.co.kr/search/search_result.asp?code3=10252&code3name=%ED%95%9C%EA%B5%AD%EA%B4%91%ED%95%99%ED%9A%8C&code4=788&code4name=%EA%B4%91%ED%95%99%EA%B3%BC+%EA%B8%B0%EC%88%A0&field=v_F0&query=%EC%96%91%EC%9E%90
*물리학과 첨단기술 2005년 12월 제14권 12호
http://www.kps.or.kr/home/webzine/webzine_list.asp?webzineUID={D546AEBF-A503-4BFA-B7A9-896FA925B978}}
그러기 위해서는 교과서를 우선 공부해야 할 필요가 있는데...
일단 이 책으로 '광학'에 무슨 개념들이 있는지 공부하고
The Light Fantastic: A Modern Introduction to Classical and Quantum Optics (Paperback)
이 책으로 '양자광학'에서 나오는 개념들을 미리 머리에 넣어두면 진행하기가 한결 수월해진다.
Quantum Optics: An Introduction (Oxford Master Series in Physics, 6)
읽어보진 않았지만 이 책도 같은 용도로 괜찮을 듯
Introduction to Quantum Optics: From Light Quanta to Quantum Teleportation (Hardcover)
실제 수식의 유도과정이나 해석에 대해서는 유명한 아래 책을 한 번 떼고나서...
The Quantum Theory of Light (Oxford Science Publications)
제대로 체력이 붙었다면 나머지 필요한 자료는 아래 Ivan H. Deutsch 교수의 수업페이지를 참고하면 다 찾을 수 있을것이다.
http://info.phys.unm.edu/~ideutsch/Classes/Phys566F08/index.htm

- Tag quantum optics, 양자광학, 외계어?, 차라리 날 죽여라
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
발 슬쩍 담그고만 있는 정도가 아니라 최소한 몸통 이상 들어가있는 연구실만 골라보았다.
*KAIST 이순칠 교수님 Magnetic Resonance & Magnetism Lab
NMR QC 하시는 분인데 지금은 다른 주제 하고계실지도 모른다. AQIS 08'때 NMR QC는 가능성이 없다고 하셨기 때문에...
*서울시립대 안도열 교수님 양자정보처리연구단
최종적으로는 실리콘QC로 가야된다고 하시는 것 같은데 홈페이지 업데이트가 안되서 요즘은 뭐하시는지 모르겠다...
*POSTECH 김윤호 교수님 Quantum Optics and Quantum Information Laboratory
SPDC로 인탱글상태를 만들어서 실험하는게 주인듯. 굳이 따지자면 실험쪽이라기보다는 실험을 이용한 이론증명쪽임.
*KAIST 이해웅 교수님 Quantum Information Research Group
이론 & 양자광학실험이 중심.
*KIAS 계산과학부 김재완 교수님 jaewan@kias.re.kr
이론중심, 이 분은 실험실 주소를 찾을 수 없었다...
일단 국내는 본격적으로 실험하는 곳 조차 그리 많지 않고 그 variety조차 엄청나게 떨어지지만 문제는 그것보다도 중심되는 국가차원의 컨소시엄 혹은 조직이 없다는 것이라 보아야 한다.
양자컴퓨터라는 단어 그자체가 일단 신기루만치 엄청 과장되어 있는 부분이 있긴 하지만 어쨌든 우리나라에서 양자컴퓨터 연구라는 건 사막에서 오아시스 찾는 느낌이다.
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
출처 : http://info.phys.unm.edu/~ideutsch/Classes/Phys566F04/index.htm

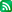
- Tag map, quantum optics
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
얼마전부터 논문접수하라고 이메일이 계속 날라오더니 퀀텀미팅에도 떴다. 사실 작년초에 우리나라에서도 QIS관련 컨퍼런스가 개최된다고 해서 엄청기대하고 십여만원에 달하는 참가비를 내고 논문을 내지도 않는데도 불구하고 참가했는데 별로 재미는 없었다. 아무래도 거의 대부분이 이론에 치우쳐져있어서 ITQC생각하고 갔더니 완전 물먹었지... 그때만해도 사실 POVM이 뭐의 약잔지도 모를 정도였으니 말 다했지...
AQIS는 아시아지역 QIS미팅인데 초기에는 이런게 별로 없어서 영향력도 있었던 모양이지만 요즘은 이런 미팅이나 컨퍼런스가 너무 많아져서 09년도는 어떨지 모르겠다. 심지어 나한테도 논문보내라고 이메일이 올 정도면 그리 인기는 없는 것 같기도 한데... 난징에서 개최된다만 그리 기대는 되지 않음.

- Tag aqis, conference
Comments List
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
US intelligence agency axes funding for work on quantum computing.
간단하게 요약하면 미국의 Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA)라는 정부기관에서 양자컴퓨터그룹에 가던 돈을 갑자기 짤랐다는 얘긴데 문제는 이 양자컴퓨터그룹이 NIST라고 이온트랩연구에 관련된 정부산하기관이고 그룹 리더는 D.J. Wineland라고 이온트랩QC에서 거의 전세계 최고라고해도 특별한 이의가 없을정도의 대가라는 사실이다.
그래서 이 블로그에서 열띤 진의논쟁이 벌어졌는데 이게 QIT/QIS 에 대한 앞으로의 정부의 인식을 보여주는것이 아니냐 하는 우려가 있었던 것 같다.
근데 내 생각에는 아무래도 그런것보다는 금년초에 발간된 A Federal Vision for Quantum Information Science 에 주목을 해야 될 것 같다.
United States National Science and Technology Council 에서 발간된 책자인데 읽어보면 QIS가 엄청 중요하다고 얘기하고 있다. 몇달만에 입장을 바꾸었다고 보기 보다는, 좀 더 자세히 읽어보면, QIS를 위한 어떤 큰 조직의 설립을 암시하고 있는 것으로 보인다. (The Call for a Coordinated Approach 부분)
그러니까 이번에 IARPA에서 돈을 짤른거는 QIS에 관한 거대통합조직 창설과정에서 예산의 재조정이 필요했기 때문에 일단 총괄적으로 회수를 한 거였던지, 아니면 그 조직의 objective에 ITQC의 priority가 높지 않았거나(현재 QC의 진행과정을 볼 때 그 가능성은 크지 않지만...) 아니면 바깥으로 나와있는 연구소에는 지원하지말고 정말로 물밑에서만 움직이기 위해 외부지원금을 잘랐거나 라고 볼 수 있을 것 같다.
다시말해 QIS가 발전가능성이 없어서, 가 아니라 QIS가 너무 중요하다고 생각했기 때문에 내려진 조치라고 생각된다는 것이다. 실제로 비공식소식통에 의하면 IARPA에서 QIS에 관한 지원금 자체는 늘어났다고 하고 있으니 당연할 듯...
참... 이번 사건으로 느끼는 거지만 정말 사회와 분리된 과학은 존재할 수 없다는 걸 새삼 절감한다. 일단 과학을 하는 주체가 인간들이고 인간들은 어떤 형태로든 반드시 사회와 연결되어 있다.
과학으로부터 파생될 수 있는 윤리적 문제, 기술활용에 관한 고민같은건 시간도 너무 많이 걸리고 철학도 없는 과학도에겐 사유하기 너무 버거운 문제이니 넘어가자고 해도 지금 당장 내 월급을 좌지우지하는 프로젝트머니를 누가 줄 것이냐 생각해보면 사실 과학자들은 과학이라는 도구만 가지고는 할 수 있는게 별로 없다. 여기서는 사회적, 정치적 문제가 들어가기 시작하는 것이다.
근데 중요한 건 이 미쳐버린 자본주의 사회에서 프로젝트 -아니면 적어도 자기 월급- 를 생각하지 않고 살 수 있는 과학자는 존재하지 않기 때문에 과학자는, 또한 과학은 사회와 완벽하게 유리될 수는 없다는 것이다. 사실 그렇게 생각하는 사람도 있는것 같아서 하는 말이다.
문제는 뭐냐? 그런 사회구조와 문제점에 대해 생각하고 자신만의 철학을 만들 시간을, 현재 고등교육과정에서는 제공하고 있지 않다는 것이다. 그저 자신의 스펙(스스로를 상품으로 가치절하시켜버리는 이 싸구려 단어도 나는 상당히 경멸하지만)으로 어떤 시험을 통과할수 있을지 여부와, 자기가 할 일이 전망이 있을까를 남에게 물어보는 값싼인생들만을 양산하게 되어버린 이 사회.
대한민국만이 그런것은 아니다. 다른 나라에 가봐도 마찬가지다. 이 지구촌이 다 미쳐있다.
예외는 언제나 존재하긴 하지만 난 general한 이야기를 하고 있는데 뜬금없이 예외를 들어 논리를 공격하는 미친넘을 존중하지 않는다.
돌파구는 언제나 존재하지 않지만 그렇다고 해도 항상 그 방법에 대해서 생각하고는 있어야 한다.
돌파구는 무엇인가.
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
- Posted
- Filed under 연구

- Tag PhD Comics
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
노벨상 딸려면 이정도 연구는 해야한다.
...?!
P.S 사진과 함께 보고싶다면 출처 로 가 보자.
|
Year |
Laureate[A] |
Country[B] |
Rationale[C] | |
|
1901 |
"[for] the discovery of the remarkable rays subsequently named after him"[8] | |||
|
1902 |
"[for] their researches into the influence of magnetism upon radiation phenomena"[9] | |||
|
| ||||
|
1903 |
"[for] his discovery of spontaneous radioactivity"[10] | |||
|
|
"[for] their joint researches on the radiation phenomena discovered by Professor Henri Becquerel"[10] | |||
|
| ||||
|
1904 |
"for his investigations of the densities of the most important gases and for his discovery of argon in connection with these studies"[11] | |||
|
1905 |
|
"for his work on cathode rays"[12] | ||
|
1906 |
|
|
"[for] his theoretical and experimental investigations on the conduction of electricity by gases"[13] | |
|
1907 |
|
"for his optical precision instruments and the spectroscopic and metrological investigations carried out with their aid"[14] | ||
|
1908 |
|
"for his method of reproducing colours photographically based on the phenomenon of interference"[15] | ||
|
1909 |
"[for] their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy"[16] | |||
|
|
| |||
|
1910 |
|
"for his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids"[17] | ||
|
1911 |
|
"for his discoveries regarding the laws governing the radiation of heat"[18] | ||
|
1912 |
"for his invention of automatic valves designed to be used in combination with gas accumulators in lighthouses and buoys"[19] | |||
|
1913 |
|
"for his investigations on the properties of matter at low temperatures which led, inter alia, to the production of liquid helium"[20] | ||
|
1914 |
|
|
"For his discovery of the diffraction of X-rays by crystals"[21] | |
|
1915 |
|
|
"For their services in the analysis of crystal structure by means of X-rays"[22] | |
|
| ||||
|
1916 |
Not awarded | |||
|
1917 |
|
"For his discovery of the characteristic Röntgen radiation of the elements"[23] | ||
|
1918 |
|
"[for] the services he rendered to the advancement of Physics by his discovery of energy quanta"[24] | ||
|
1919 |
|
|
"for his discovery of the Doppler effect in canal rays and the splitting of spectral lines in electric fields"[25] | |
|
1920 |
|
"[for] the service he has rendered to precision measurements in Physics by his discovery of anomalies in nickel steel alloys"[26] | ||
|
1921 |
|
"for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect"[27] | ||
|
1922 |
"for his services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them"[28] | |||
|
1923 |
|
"for his work on the elementary charge of electricity and on the photoelectric effect"[29] | ||
|
1924 |
|
|
"for his discoveries and research in the field of X-ray spectroscopy"[30] | |
|
1925 |
|
"for their discovery of the laws governing the impact of an electron upon an atom"[31] | ||
|
|
| |||
|
1926 |
|
"for his work on the discontinuous structure of matter, and especially for his discovery of sedimentation equilibrium"[32] | ||
|
1927 |
|
"for his discovery of the effect named after him"[33] | ||
|
|
"for his method of making the paths of electrically charged particles visible by condensation of vapour"[33] | |||
|
1928 |
|
"for his work on the thermionic phenomenon and especially for the discovery of the law named after him"[34] | ||
|
1929 |
|
"for his discovery of the wave nature of electrons"[35] | ||
|
1930 |
|
"for his work on the scattering of light and for the discovery of the effect named after him"[36] | ||
|
1931 |
Not awarded | |||
|
1932 |
|
"for the creation of quantum mechanics, the application of which has, inter alia, led to the discovery of the allotropic forms of hydrogen"[37] | ||
|
1933 |
"for the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory"[38] | |||
|
| ||||
|
1934 |
Not awarded | |||
|
1935 |
|
|
||
|
1936 |
|
"for his discovery of cosmic radiation"[40] | ||
|
|
||||
|
1937 |
|
|
"for their experimental discovery of the diffraction of electrons by crystals"[41] | |
|
|
| |||
|
1938 |
|
"for his demonstrations of the existence of new radioactive elements produced by neutron irradiation, and for his related discovery of nuclear reactions brought about by slow neutrons"[42] | ||
|
1939 |
|
"for the invention and development of the cyclotron and for results obtained with it, especially with regard to artificial radioactive elements"[43] | ||
|
1940 |
Not awarded | |||
|
1941 |
Not awarded | |||
|
1942 |
Not awarded | |||
|
1943 |
|
|
"for his contribution to the development of the molecular ray method and his discovery of the magnetic moment of the proton"[44] | |
|
1944 |
|
|
"for his resonance method for recording the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei"[45] | |
|
1945 |
|
"for the discovery of the Exclusion Principle, also called the Pauli principle"[46] | ||
|
1946 |
|
|
"for the invention of an apparatus to produce extremely high pressures, and for the discoveries he made there within the field of high pressure physics"[47] | |
|
1947 |
|
"for his investigations of the physics of the upper atmosphere especially for the discovery of the so-called Appleton layer"[48] | ||
|
1948 |
|
|
"for his development of the | |
|
1949 |
"for his prediction of the existence of mesons on the basis of theoretical work on nuclear forces"[50] | |||
|
1950 |
|
|
"for his development of the photographic method of studying nuclear processes and his discoveries regarding mesons made with this method"[51] | |
|
1951 |
|
|
"for their pioneer work on the transmutation of atomic nuclei by artificially accelerated atomic particles"[52] | |
|
|
||||
|
1952 |
|
"for their development of new methods for nuclear magnetic precision measurements and discoveries in connection therewith"[53] | ||
|
|
| |||
|
1953 |
|
|
"for his demonstration of the phase contrast method, especially for his invention of the phase contrast microscope"[54] | |
|
1954 |
|
|
"for his fundamental research in quantum mechanics, especially for his statistical interpretation of the wavefunction"[55] | |
|
|
"for the coincidence method and his discoveries made therewith"[55] | |||
|
1955 |
|
|
"for his discoveries concerning the fine structure of the hydrogen spectrum"[56] | |
|
|
|
"for his precision determination of the magnetic moment of the electron"[56] | ||
|
1956 |
|
|
"for their researches on semiconductors and their discovery of the transistor effect"[57] | |
|
|
| |||
|
| ||||
|
1957 |
"for their penetrating investigation of the so-called parity laws which has led to important discoveries regarding the elementary particles"[58] | |||
|
Republic of | ||||
|
1958 |
|
"for the discovery and the interpretation of the Cherenkov effect"[59] | ||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
1959 |
|
|
"for their discovery of the antiproton"[60] | |
|
|
| |||
|
1960 |
|
"for the invention of the bubble chamber"[61] | ||
|
1961 |
|
|
"for his pioneering studies of electron scattering in atomic nuclei and for his thereby achieved discoveries concerning the structure of the nucleons"[62] | |
|
|
"for his researches concerning the resonance absorption of gamma radiation and his discovery in this connection of the effect which bears his name"[62] | |||
|
1962 |
|
|
"for his pioneering theories for condensed matter, especially liquid helium"[63] | |
|
1963 |
|
|
"for his contributions to the theory of the atomic nucleus and the elementary particles, particularly through the discovery and application of fundamental symmetry principles"[64] | |
|
|
|
"for their discoveries concerning nuclear shell structure"[64] | ||
|
| ||||
|
1964 |
|
|
"for fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics, which has led to the construction of oscillators and amplifiers based on the maser-laser principle"[65] | |
|
| ||||
|
|
| |||
|
1965 |
|
|
"for their fundamental work in quantum electrodynamics, with deep-ploughing consequences for the physics of elementary particles"[66] | |
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
1966 |
|
|
"for the discovery and development of optical methods for studying Hertzian resonances in atoms"[67] | |
|
1967 |
|
"for his contributions to the theory of nuclear reactions, especially his discoveries concerning the energy production in stars"[68] | ||
|
1968 |
|
|
"for his decisive contributions to elementary particle physics, in particular the discovery of a large number of resonance states, made possible through his development of the technique of using hydrogen bubble chamber and data analysis"[69] | |
|
1969 |
|
"for his contributions and discoveries concerning the classification of elementary particles and their interactions"[70] | ||
|
1970 |
|
|
"for fundamental work and discoveries in magneto-hydrodynamics with fruitful applications in different parts of plasma physics"[71] | |
|
|
|
"for fundamental work and discoveries concerning antiferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism which have led to important applications in solid state physics"[71] | ||
|
1971 |
|
|
"for his invention and development of the holographic method"[72] | |
|
1972 |
|
|
"for their jointly developed theory of superconductivity, usually called the BCS-theory"[73] | |
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
1973 |
|
|
"for their experimental discoveries regarding tunneling phenomena in semiconductors and superconductors, respectively"[74] | |
|
| ||||
|
|
|
"for his theoretical predictions of the properties of a supercurrent through a tunnel barrier, in particular those phenomena which are generally known as the Josephson effect"[74] | ||
|
1974 |
|
|
"for their pioneering research in radio astrophysics: Ryle for his observations and inventions, in particular of the aperture synthesis technique, and Hewish for his decisive role in the discovery of pulsars"[75] | |
|
| ||||
|
1975 |
|
|
"for the discovery of the connection between collective motion and particle motion in atomic nuclei and the development of the theory of the structure of the atomic nucleus based on this connection"[76] | |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
1976 |
|
"for their pioneering work in the discovery of a heavy elementary particle of a new kind"[77] | ||
|
| ||||
|
1977 |
|
"for their fundamental theoretical investigations of the electronic structure of magnetic and disordered systems"[78] | ||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
1978 |
|
|
"for his basic inventions and discoveries in the area of low-temperature physics"[79] | |
|
|
"for their discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation"[79] | |||
|
|
| |||
|
1979 |
|
"for their contributions to the theory of the unified weak and electromagnetic interaction between elementary particles, including, inter alia, the prediction of the weak neutral current"[80] | ||
|
|
||||
|
| ||||
|
1980 |
|
"for the discovery of violations of fundamental symmetry principles in the decay of neutral K-mesons"[81] | ||
|
|
| |||
|
1981 |
|
|
"for their contribution to the development of laser spectroscopy"[82] | |
|
| ||||
|
|
|
"for his contribution to the development of high-resolution electron spectroscopy"[82] | ||
|
1982 |
|
|
"for his theory for critical phenomena in connection with phase transitions"[83] | |
|
1983 |
|
|
"for his theoretical studies of the physical processes of importance to the structure and evolution of the stars"[84] | |
|
|
|
"for his theoretical and experimental studies of the nuclear reactions of importance in the formation of the chemical elements in the universe"[84] | ||
|
1984 |
|
"for their decisive contributions to the large project, which led to the discovery of the field particles W and Z, communicators of weak interaction"[85] | ||
|
|
| |||
|
1985 |
|
"for the discovery of the quantized Hall effect"[86] | ||
|
1986 |
|
|
"for his fundamental work in electron optics, and for the design of the first electron microscope"[87] | |
|
|
"for their design of the scanning tunneling microscope"[87] | |||
|
| ||||
|
1987 |
|
|
"for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials"[88] | |
|
| ||||
|
1988 |
|
"for the neutrino beam method and the demonstration of the doublet structure of the leptons through the discovery of the muon neutrino"[89] | ||
|
|
| |||
|
| ||||
|
1989 |
|
|
"for the invention of the separated oscillatory fields method and its use in the hydrogen maser and other atomic clocks"[90] | |
|
|
|
|||
|
| ||||
|
1990 |
|
|
"for their pioneering investigations concerning deep inelastic scattering of electrons on protons and bound neutrons, which have been of essential importance for the development of the quark model in particle physics"[91] | |
|
| ||||
|
1991 |
|
"for discovering that methods developed for studying order phenomena in simple systems can be generalized to more complex forms of matter, in particular to liquid crystals and polymers"[92] | ||
|
1992 |
|
|
"for his invention and development of particle detectors, in particular the multiwire proportional chamber"[93] | |
|
1993 |
|
|
"for the discovery of a new type of pulsar, a discovery that has opened up new possibilities for the study of gravitation"[94] | |
|
|
| |||
|
1994 |
|
|
"for the development of neutron spectroscopy" and "for pioneering contributions to the development of neutron scattering techniques for studies of condensed matter"[95] | |
|
|
"for the development of the neutron diffraction technique" and "for pioneering contributions to the development of neutron scattering techniques for studies of condensed matter"[95] | |||
|
1995 |
|
"for the discovery of the tau lepton" and "for pioneering experimental contributions to lepton physics"[96] | ||
|
|
"for the detection of the neutrino" and "for pioneering experimental contributions to lepton physics"[96] | |||
|
1996 |
|
|
"for their discovery of superfluidity in helium-3"[97] | |
|
| ||||
|
|
| |||
|
1997 |
|
"for development of methods to cool and trap atoms with laser light"[98] | ||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
1998 |
|
"for their discovery of a new form of quantum fluid with fractionally charged excitations"[99] | ||
|
| ||||
|
|
| |||
|
1999 |
|
"for elucidating the quantum structure of electroweak interactions in physics"[100] | ||
|
|
| |||
|
2000 |
"for developing semiconductor heterostructures used in high-speed- and optoelectronics"[101] | |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
"for his part in the invention of the integrated circuit"[101] | ||
|
2001 |
|
"for the achievement of Bose-Einstein condensation in dilute gases of alkali atoms, and for early fundamental studies of the properties of the condensates"[102] | ||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
2002 |
|
|
"for pioneering contributions to astrophysics, in particular for the detection of cosmic neutrinos"[103] | |
|
| ||||
|
|
"for pioneering contributions to astrophysics, which have led to the discovery of cosmic X-ray sources"[103] | |||
|
2003 |
|
"for pioneering contributions to the theory of superconductors and superfluids"[104] | ||
|
|
| |||
|
| ||||
|
2004 |
|
"for the discovery of asymptotic freedom in the theory of the strong interaction"[105] | ||
|
|
| |||
|
| ||||
|
2005 |
|
"for his contribution to the quantum theory of optical coherence"[106] | ||
|
|
|
"for their contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb technique"[106] | ||
|
| ||||
|
2006 |
|
"for their discovery of the blackbody form and anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background radiation"[107] | ||
|
| ||||
|
2007 |
|
"for the discovery of giant magnetoresistance"[108] | ||
|
| ||||
|
2008 |
|
"for the discovery of the origin of the broken symmetry which predicts the existence of at least three families of quarks in nature"[109] | ||
|
| ||||
|
|
"for the discovery of the mechanism of spontaneous broken symmetry in subatomic physics"[109] | |||
- Posted
- Filed under 연구

- Tag conference
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
상당히 직관적으로 표현된 것 같아서 올려본다... 저작권에 걸리는건 아니겠지-_-?
촐처 : IEEE Spectrum: The Trap Technique
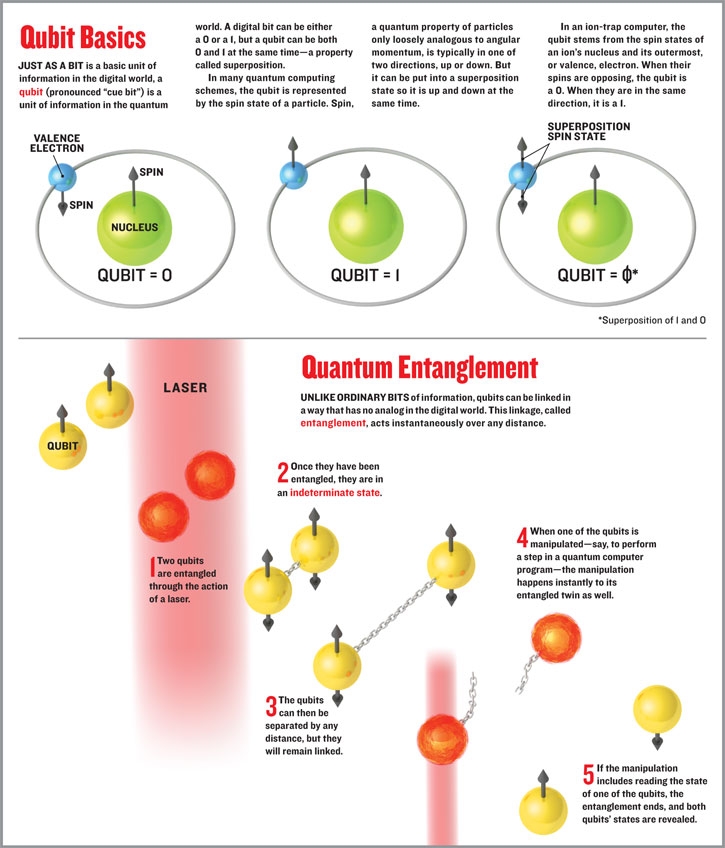
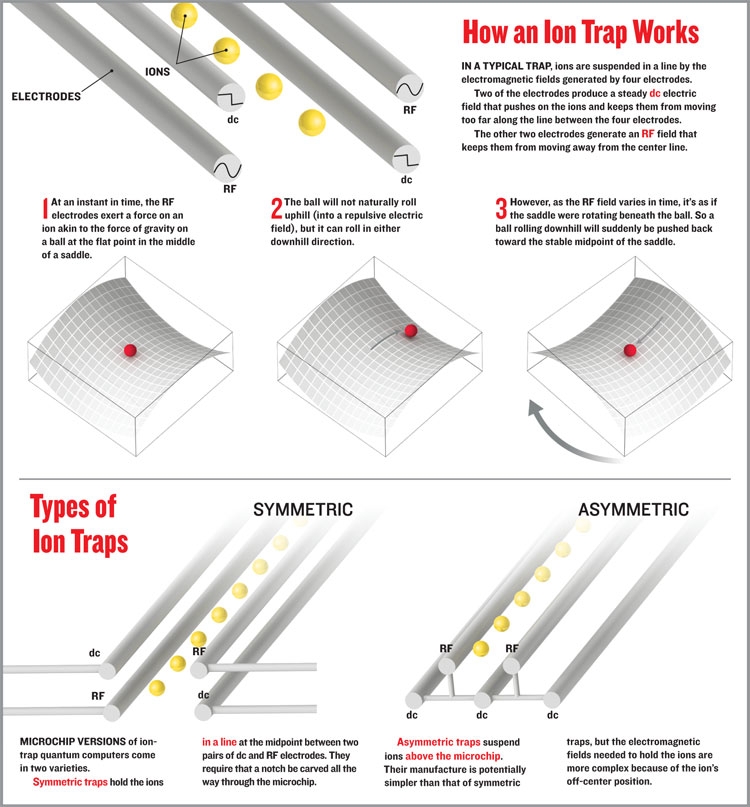
Rotating saddle을 동영상으로 보고 싶으면 아래 URL을 참조
http://iontrap.umd.edu/research/microspheres/Rotating%20Saddle.MOV
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
함수개형 좀 볼려고 프로그램 괜찮은게 있나 찾아봤는데 matlab 이나 mathmatica를 쓰라고 하는데 이런것까지는 필요없고 가벼운게 없나 찾아봤더니 Gnuplot라는 프로그램이 있더라.
*다운로드는 여기서
http://sourceforge.net/project/showfiles.php?group_id=2055&package_id=1996
*사용설명서
http://coffeenix.net/doc/gnuplot/gnuplot.html
위 사이트의 원본은 여기
http://www.cnu.ac.kr/~byung/Softwares/gnuplot/TOC.htm
한국어 사용설명서 위키(번역참여를 원하고 있다)
http://snowrain.kr/snowall/kgm/wiki.php

- Tag gnuplot, 그래프 그리는 프로그램
- Posted
- Filed under 연구

사실 번역해볼까 했는데 그게 무슨 의미가 있겠나 싶어서 그냥 링크만 포스팅.
무엇보다 삽입된 Figure가 너무 웃겨서 한 번 따와봤다. 이온트랩 양자 컴퓨터란 바로 이런것이야!!!(<-뻥)
http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=quantum-computing-with-ions
찾아보니 번역하신 분이 계시다...
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
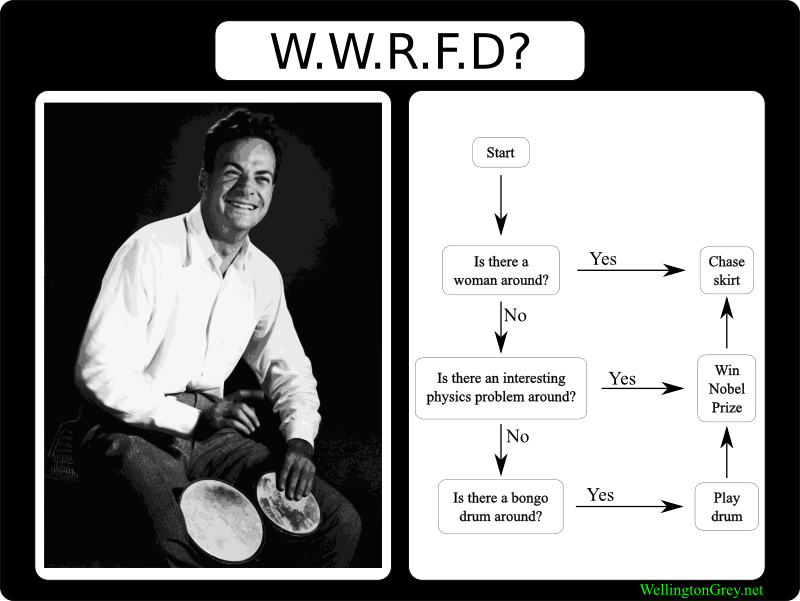
(1) write down the problem;
(2) think very hard;
(3) write down the answer.
파인만은 대부분의 문제를 파인만 알고리즘으로 풀었다고 한다. 파인만에게밖에 적용 안되기 때문에 파인만 알고리즘이라 함.
*파인만 교수 위키페이지(위키내용이 이렇게 빡빡하게 들어찬 사람도 드물지...역시 포스가 느껴진다)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Richard_feynman
아래는 웹서핑 중 발견한 '리처드 파인만이란 인간은 평소에 뭘 하고 살았나?'
What Would Richard Feynman Do?
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
*Raman transition
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raman_transition
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raman_scattering
http://www.hanmilab.co.kr/neboard/Board.aspx?bno=001004&mode=VIEW&goto=1&idxno=122&reply=0
*Selection rule
Selection rule 과 Doppler broadning에 관한 강의노트
*Monte Carlo method
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monte_Carlo_method
*Plasma
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plasma_(physics)
*Symmetry Breaking
http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/symmetry-breaking/
*Quadrupole
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/Hbase/electric/elequad.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quadrupole
-Quadrapole transition :
A transition of an atom or molecule from one energy state to another, in which electric quadrupole radiation is emitted or absorbed.
*Solid angle
http://www.skyobserver.net/zbxe/astro_concepts/5968
http://www.sjsu.edu/faculty/watkins/solidangle.htm
*Many-Body Problem
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/N-body_problem
*Fock state
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fock_state
*Root mean square
http://ask.nate.com/qna/view.html?n=4500651
*SI 접두어 및 그리스 문자 읽는 법
http://dream731.tistory.com/29
*Tensor
http://www.encyber.com/search_w/ctdetail.php?gs=ws&gd=&cd=&d=&k=&inqr=&indme=&p=1&q=&masterno=155273&contentno=155273
http://www.scieng.net/zero/view.php?id=tech&page=4&category=&sn=off&ss=on&sc=on&keyword=&select_arrange=hit&desc=desc&no=1972

- Tag 외계어란 바로 이런것, 차라리 날 죽여라
- Posted
- Filed under 연구
1. Feynman Lectures on Physics I, II, III
영어가 60년대 미국 생활영어라서 읽기는 까다롭지만 좋은 책.
I은 고전역학, II는 전자기학, III은 양자역학
Feynman이 살아생전에 칼텍 학생들 가르친걸 녹음떠다가 지은 책
2. Fundamentals of Physics
물리학 입문의 바이블 (잔소리 필요없음)
3. Electricity and Magnetism (Reitz)
하도 오랫동안 안본 책이라 제목이 맞는지는 까먹었음
전자기학을 잘 설명한 책
4. Classical Dynamics (Marion)
고전역학을 잘 설명한 책
다른 책보다 처음은 어렵게 시작하지만 많은 도움이 됨
깔끔한 기술이 돋보임
5. Mathematical Method for Physicists (Arfken)
수리물리 교재의 Bible. 이 책 한권에는 물리에 쓰이는 거의 모든 수학이 망라
두고두고 보면서 풀면서 음미해 볼만한 책
6. Quantum Mechanics (Liboff)/양자역학 (송희성)
두 책 모두 권하고 싶은 책.
이 두 권을 제대로 이해하면 이제 슬슬 물리에서 뭐하는지 감이 잡힘.
요기까지 제대로 넘어야 이제 물리에 대해 제대로 된 질문을 할 수 있음.
7. Fundamentals of Statistical Mechanics (Reif)
통계물리에서 시작해서 열물리로 넘어가는
현대적인 기술 방법임. 너무너무 권장함.
일단 여기까지 오면 물리학에서 배워야 할 기본적인 것을 간신히 배웠다고
할 수 있음. 이때가 3학년 2학기임
저 책들을 볼때는 1. 의 Vol 1 과 2.를 같이 보도록 하고
2.의 초반이 끝나갈 무렵부터는 4.를 같이 보기 시작하면 좋음
즉, 고전 역학을 위해 3권 정도로 기초를 튼튼히..
3. 과 1.의 Vol II와는 같이 볼것.
3.과 Vol II가 중반이 넘어가면 수학을 다지기 위해 5를 보기 시작
이 과정이 끝나면
1. Vol III와 6을 같이 볼것
즉, 3권 정도
그러면서 동시에 7을 같이 봐야 할 것임.
그리고 1 단계를 위해서 필요한 수학을 나열하면
1. 미분적분학
2. 해석학
3. 미분방정식
4. 선형대수
5. 복소해석학
대충 이 5가지의 수학은 거의 필수이고
5.를 보게 되면 어떤 수학이 필요한지가 잘 드러나니깐
그 후로는 스스로 책을 고를 수 있을 것임
이렇게 기초만 3년 다지고
고체물리, 핵물리, 광학 등등으로 나뉘게 되는데
이 분야들은 앞에서 배운걸 동시에 써먹기 때문에
기초를 제대로 해두지 않으면 별나라 예기로 들릴 것임.
여기까지 배우면 학부는 대충 마치는 것이고
대학원에 들어가게 되면 배우는 것은
역시
1. 고전역학
2. 전자기학
3. 양자역학
4. 통계물리학
을 또 다시 배움 연구할 때는 이 정도는 봐야 기초가 됨
참고 교재로
1. Classical Mechanics (Goldstein)/Mechanics (Landau)
2. Classical Electrodynamics (Jackson)
3. Mordern Quantum Mechanics (Sakurai)
5. 아직 바이블이라고 할 교재가 없음
아 위에 4가 아니라 5임
대충 요렇게 또 기초를 닦으면 다 될거 같지만
또다른 수준의 기초가 필요함
즉, 양자장 이론이라는 것인데
소개 할 만학 책이
두 부류로 나뉨
하나는 입자물리쪽이고 다른 하나는 다체이론쪽임
1. Advanced Quantum Mechanics (Sakurai)
2. An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory (Sterman)
3. Quantum Many Particles (Fetter and Wallecker)
4. Quantum Many Particle System (Negel and Orlando)
그리고 Bjorkan의 책이 있지만 권하지 않음
여기에서는 상당히 복잡한 수학이 나오는데
도움이 될만한 책은
1. Group Theory In Physics (누구?)
2. Topology (Munkres)
등등이 있음
*역학
more..
*전자기학
more..
*양자역학
more..
*통계역학
more..
*수리물리학
more..
 HighImpedanceprobe.doc
HighImpedanceprobe.doc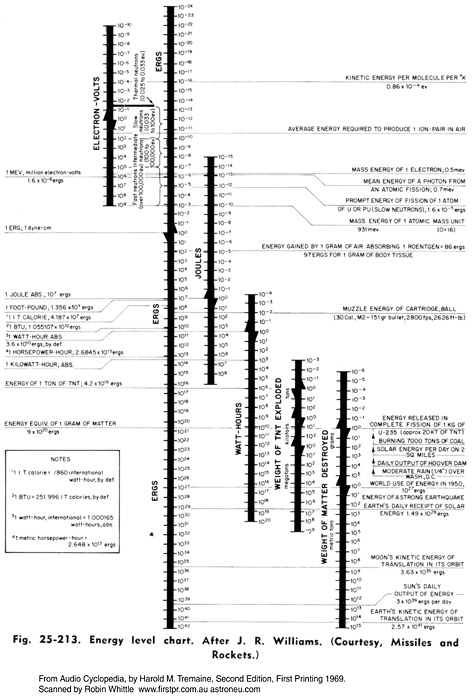
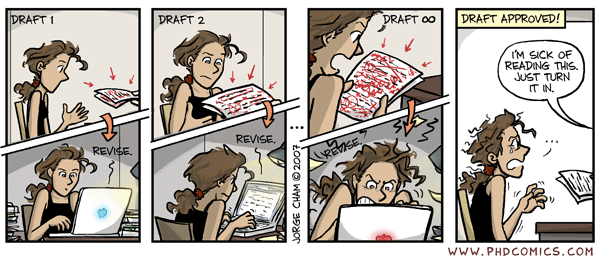
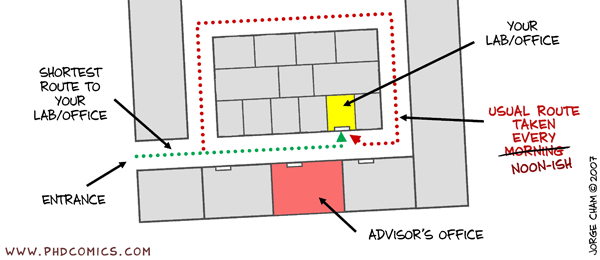
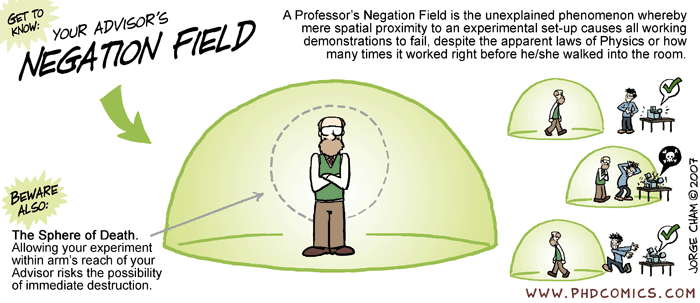





Comments List
오~~멋진걸 하는뎅???ㅎㅎ
나도 이번에 연료전지 실험 한걸로 논문 쓰고 있는중~^^ㅎㅎ
화이팅이당~~^^//
ㅋㅋ화이팅염